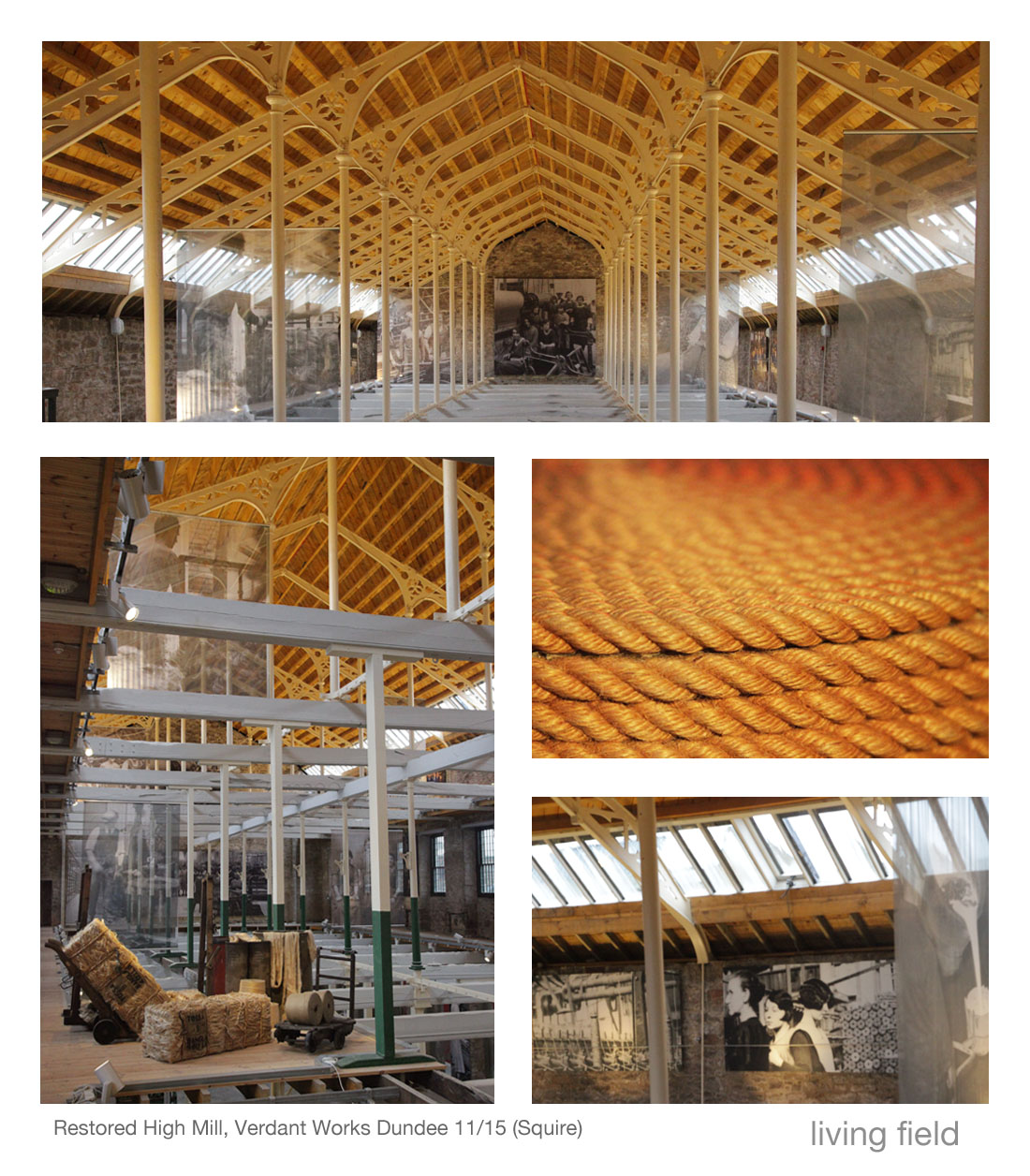
T rep. The short form given by our field survey teams to white clover Trifolium repens. Still a common plant of pasture and waysides, so common that the intricacies of its structure and  function generally go unnoticed.
function generally go unnoticed.
Yet the mathematical artworks by Macoto Murayama shown in July at Dundee University reveal these intricacies in astonishing detail (image right).
The exhibition was held by courtesy of Frantic Gallery, Tokyo.
The Living Field’s correspondent gk-images sent some cellphone snaps from the exhibition.
The introduction gives some detail of the artist and how he transfers the complex flowering heads and flowers of his botanical subjects to two-dimentional images.
“Macoto Murayama is a Japanese artist who cultivates ‘inorganic flora’. His extraordinary images are created after minutely dissecting real flowers and studying [them] under a microscope. His 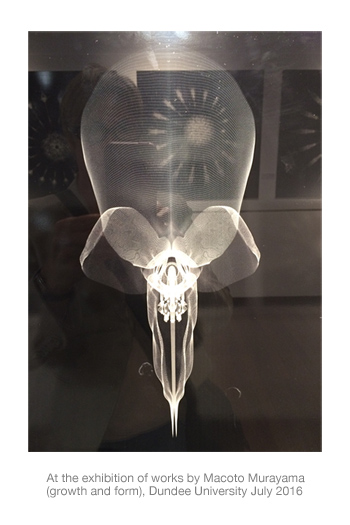 drawings are then modelled in 3D imaging software then rendered into 2D compositions on photoshop before being printed on a large scale.”
drawings are then modelled in 3D imaging software then rendered into 2D compositions on photoshop before being printed on a large scale.”
Born in Kanagawa, Japan in 1984 he is now a researcher at Institute of Advanced Media and Art and Sciences, Tokyo.
The photographs, with reflections of lights and the opposite wall are of white clover (top) and spanish broom (lower).
Sources, links
Dundee University – Macoto Murayama: Growth and Form Exhibition. 14 May to 20 August 2016. Lamb Gallery, Tower Building, Dundee. Click the link for opening times.
Macoto Murayama at Frantic gallery: http://frantic.jp/en/artist/artist-murayama.html
Frantic Gallery Tokyo. Looks like some great exhibitions, for example the Universe and other Oddities by Zen Tainaka.
On Growth and form, a classic treatise by D’Arcy Thompson. Web site http://www.darcythompson.org/about.html
Images Thanks to gk-images for the photographs shown here.
Ps Back to T. rep. There would be, in the 1940s, five or six legumes growing as ‘weeds’ in cornfields but they have since been ousted by nitrogen fertiliser and chemical herbicide. Trifolium repens is one of the the last remaining of these nitrogen fixers still found, but then rarely, in arable fields.








